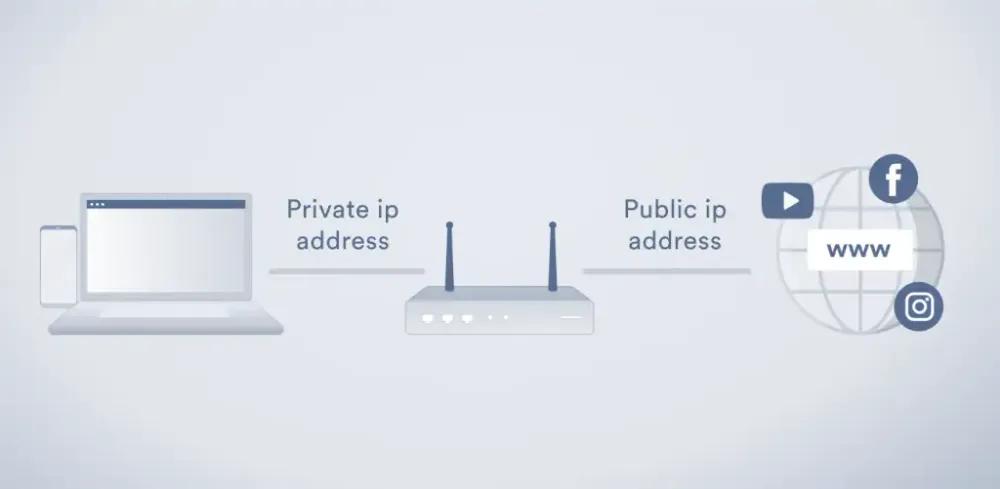
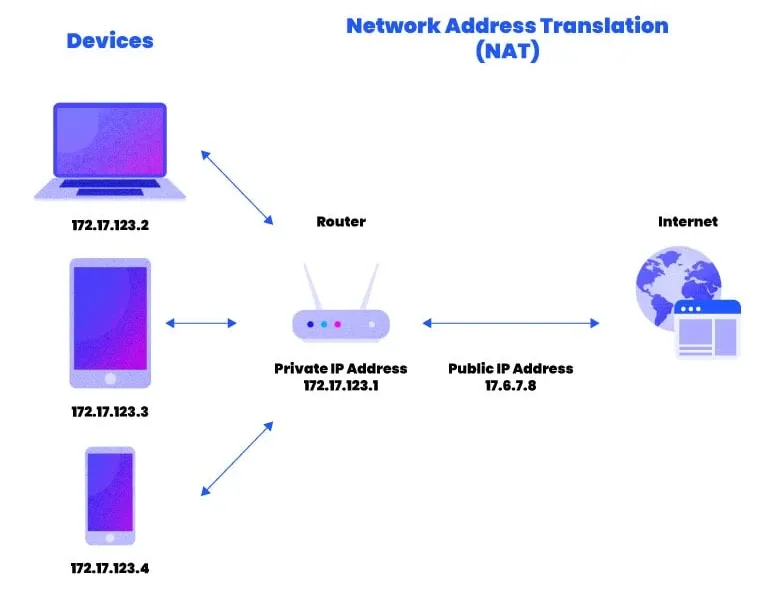
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a process that converts private IP addresses into public IP addresses when devices within a company, home, or classroom need to communicate with the outside world. In the following section, we will explore the fundamentals of NAT (Network Address Translation) and evaluate its pros and cons.
Definition of NAT
NAT (Network Address Translation) is a network address translation technology used to convert the IP address of a private network into an IP address identifiable by the public network, or convert the IP address of the public network into an IP address identifiable by the private network.
Why use NAT?
IPv4 addresses are scarce. Although using unclassified addresses can temporarily slow down the depletion of IPv4 addresses, the rapid growth rate of Internet users remains a significant concern, putting IPv4 addresses at risk of exhaustion.
Therefore, a method called network address translation (NAT) was proposed to alleviate the problem of IPv4 address exhaustion
How NAT works
When devices on the internal network (such as computers, mobile phones) need to access the external network (such as the Internet), they send data packets to the IP address of the target device.
At the boundary between the internal network and the external network, there is a NAT device (usually a router). When this device receives a packet from the internal network, it checks the packet's destination IP address.
If the destination IP address is an address on the external network, the NAT device will convert the source IP address from the private IP address of the internal network device to the IP address exposed by the NAT device. At the same time, the NAT device will record this mapping relationship so that it can perform reverse conversion when responding to data packets returned from the external network.
The NAT device sends the converted packets to the external network. In this way, devices on the external network will think that the data comes from the IP address exposed by the NAT device.
When a device on the external network sends a response to the IP address exposed by the NAT device, the NAT device will look up the previously recorded mapping relationship, convert the target IP address from the public IP address to the private IP address of the corresponding internal network device, and send the response The packet is forwarded to the internal network.
With NAT, internal networks can share a small number of public IP addresses because the private IP addresses of internal devices are mapped to public IP addresses. This technology helps solve the problem of insufficient IPv4 addresses while providing a level of security because external networks cannot directly access the private IP addresses of internal network devices.
Type of NAT
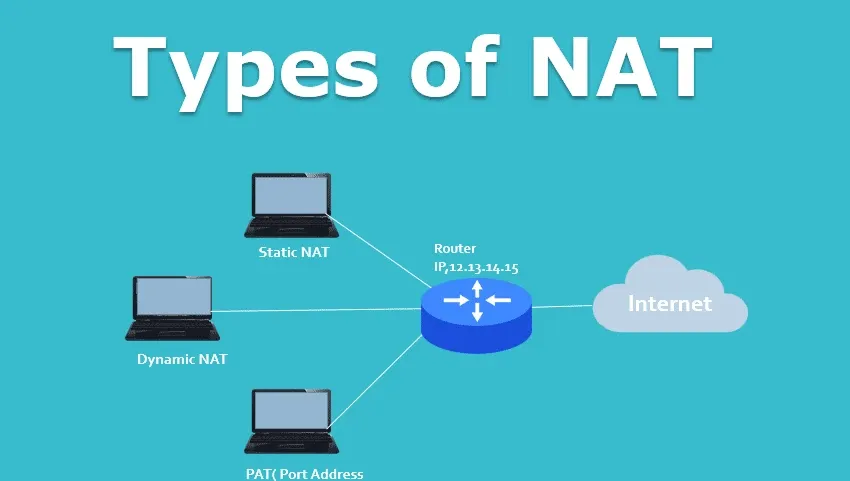
There are three main types of NAT:
-
Static NAT: One-to-one mapping, mapping a fixed IP address on the internal private network to a fixed IP address on the external public network.
-
Dynamic NAT: Dynamically allocate public IP addresses to devices in the internal private network, and dynamically allocate IP addresses according to the needs of the devices. When the device no longer needs to be connected, the IP address is released and can be assigned to other devices.
-
PAT (Port Address Translation, also known as NAT Overload): Map the IP addresses of multiple internal private network devices to a single public IP address, and distinguish these devices through different port numbers. This approach enables many-to-many mapping and more efficient use of public IP addresses.
The role of NAT
-
Address Hiding: By hiding the real IP address of the internal private network behind the public network, the security of the network is improved because the external network cannot directly access the real IP address of the internal network.
-
IP Address Reuse: Allows multiple internal devices to share one or a few public IP addresses, saving the use of IP addresses.
-
Transition Technology: In the case of IPv4 exhaustion, NAT can help transition between IPv4 and IPv6 and realize the interoperability of IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
NAT advantages and disadvantages
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a network technology used to map IP addresses within a private network to IP addresses on a public network, allowing multiple devices to share a single public IP address. This technology is mainly used in IPv4 networks because IPv4 address resources are limited, and NAT can help solve the problem of IP address shortage. The following are the advantages and disadvantages of NAT:
advantage:
-
IP Address Savings: NAT allows multiple internal devices to share one or a set of public IP addresses.
-
Network security enhancement: NAT acts as a firewall, hiding the real IP address of the internal network so that the internal network cannot be directly accessed from the outside, thus improving security.
shortcoming:
-
Communication Complexity: NAT introduces additional complexity because it requires maintaining translation tables to track mappings between internal and external IP addresses, potentially impacting network performance and increasing network latency.
-
Application Limitations: Some applications and services may not work properly or require special configuration to accommodate NAT. Especially for some services that require direct external access, such as video conferencing, P2P applications, etc.
-
Not conducive to end-to-end connections: NAT will destroy the principle of end-to-end connection, making it impossible for some applications to directly establish peer-to-peer connections, and additional measures need to be taken, such as port forwarding (Port Forwarding).
NAT improvements
- Use IPv6:
The range of available IPv6 addresses is so vast that every device can have a public IP address, but it will take time for IPv6 to become widely adopted.
- NAT penetration technology:
NAT penetration technology enables network applications to identify and obtain the public IP address of a NAT device they are behind. This allows them to establish port mapping entries for themselves. Note that these actions are automatically performed by the application running behind the NAT device.

